SUMMARY – INTERFACE DESIGN REVIEW
This weeks lecture was discussing an overview of the past weeks lectures. but also highlighting design principles within the interactive design concept.
Covering topics and exploring interface design.
Revision of the fundamentals and principles of the interface designs.
- Visual Focus
- Problem Solving
- Contextual
- Conceptual
- Wholeness
- Linear and no linear
What is an interface?
- A point where two systems, subjects, organisations, etc. meet and interact.
- Interact with another system and or person.
REFLECTION
Gestalt psychology / visual thinking?
- Gestalt is a collection of theories of the mind, developed by the Gestalt School of Psychology at the Berlin School in the late 1880s.
- We visually see things as objects at first glance, we see a shape rather than the actual individual parts of the object itself.
Gestalt 7 Visual Principales
Proximity
- The distance between elements, the white space and grouping of familiar objects.
Symmetry
- Organising objects and elements that are similar to each other to perhaps create familiarity for the user.
Closure
- The white space and good readably of the elements and objects on the screen.
Similarity
- Similar to symmetry, similarly is creating / organising objects and elements that can be grouped to appear similar. Intensionally creating familiarity for the user.
Common Fate
- Active buttons / tabs can be an example of common fate, because they should have a receptiveness to them in the layout of a design.
Continuity
- Is the repetition of elements or objects within the design layout. It is the natural flow of designed elements.
Figure and Ground
- When our mind separates the visual objects into the foreground and other objects into the background.
REFERENCES AND IMAGES
http://digitology.co.uk/services/design_usability.php
http://www.designyourway.net/drb/user-interface-design-inspiration-40-ui-design-examples/
http://blog.fusioncharts.com/2014/03/how-to-use-the-gestalt-principles-for-visual-storytelling-podv/








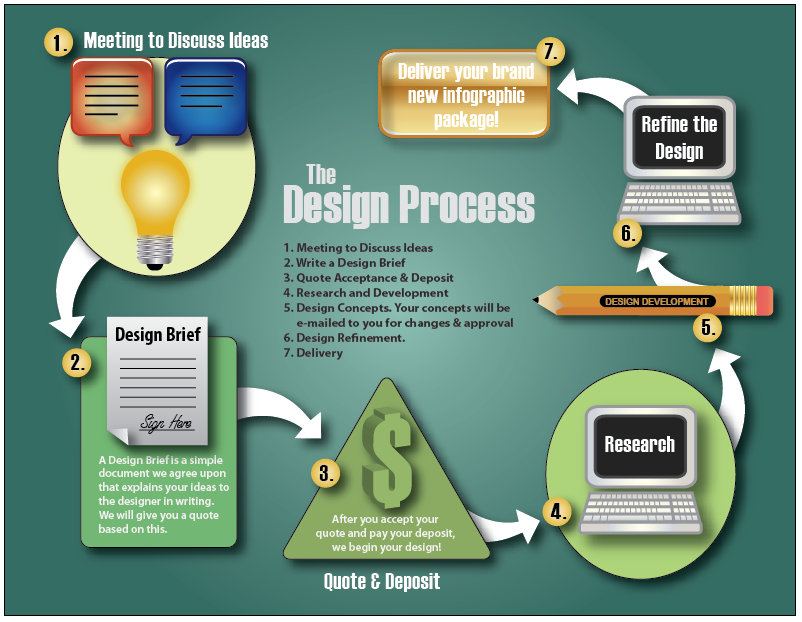







 15 web sites with excellent UX
15 web sites with excellent UX